Definition:
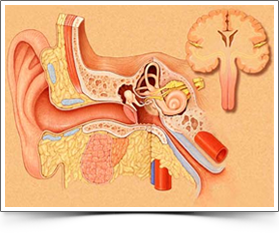
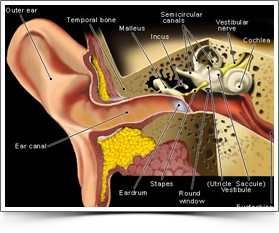
Vertigo is a subjective sense of imbalance. It is an illusion of motion such as rotating, tilting or shifting. The patient feels as if the motion is within his head or that the objects in the surroundings are moving or tilting.
Symptoms:
Patient’s main complaint is Giddiness. They may have associated symptoms like deafness, tinnitus (hearing sound in absence of external stimulus), nausea, vomiting, double vision, blurring of vision, numbness of face, headache, sudden falling and loss of consciousness.
Causes of Vertigo:
Vertigo indicates a problem within the inner ear. Inner ear diseases like benign paroxysmal positional Vertigo, Meniere`s disease and vestibular Neuronitis are some of the common causes of vertigo. Central causes like Hypoxia of Brain, Tumours of Brain, Cerebellar diseases, and diseases of blood vessels of the brain can also cause Vetigo.
Risk Factors:
Thyroid disease, Hypertension, Diabetes mellitus, anaemia, decreased supply of blood to brain from posture related low blood pressure (postural hypotension) or cardiac arrhythmias can lead to dizziness or vertigo.
A myriad of medications including those used to treat high blood pressure, high blood sugar and cardiac arrhythmias can also predispose a person to vertigo. Even psychogenic disorders like anxiety disorders, panic syndromes can lead to vertigo.
Diagnosis:
 Examination of ear
Examination of ear Cerebellar function tests
Cerebellar function tests Balance tests – It begins when the patient walks into the room.
Balance tests – It begins when the patient walks into the room. Electronystagmography – it records eye movements during various neck and eye movements. It is the most important investigation for Vertigo. It helps to differentiate between central and peripheral vertigo. In peripheral vertigo it helps us to know which ear is involved. It also involves caloric testing. Here the recordings are made when the external auditory canal is irrigated with warm water at 440c and cold water at 300c.
Electronystagmography – it records eye movements during various neck and eye movements. It is the most important investigation for Vertigo. It helps to differentiate between central and peripheral vertigo. In peripheral vertigo it helps us to know which ear is involved. It also involves caloric testing. Here the recordings are made when the external auditory canal is irrigated with warm water at 440c and cold water at 300c. Examination of cranial nerves.
Examination of cranial nerves. CT Scan and MRI of skull and Brain.
CT Scan and MRI of skull and Brain.
Treatment:
Conservative:
 Treatment or elimination of the cause.
Treatment or elimination of the cause. Low salt diet and diuretics.
Low salt diet and diuretics. Suppression of the vestibular system by Labyrinthine sedatives.
Suppression of the vestibular system by Labyrinthine sedatives. Suppression of patient’s emotional reaction by mild tranquilizers.
Suppression of patient’s emotional reaction by mild tranquilizers. Wait for compensation. Compensation can be hastened by specific vestibular exercises.
Wait for compensation. Compensation can be hastened by specific vestibular exercises. Acceptance of the problem and using appropriate aids like walking stick.
Acceptance of the problem and using appropriate aids like walking stick.
Surgical:
It is rarely used. It also depends on the cause of Vertigo. It is indicated in cases resistant to Conservative management. The various options available are Vestibular nerve section, and destruction of balance organ in the inner ear (labyrinthectomy) by chemical or surgical method. If the cause of Vertigo is an Intracranial then the disease is treated accordingly.